-
 Industry News- Why is the Transfer Film Mechanism of a self lubricat...
Industry News- Why is the Transfer Film Mechanism of a self lubricat...In high-load and low-speed industrial applications, the transition toward maintenance-free components has prioritized the engineering of the...
-
 Industry News- Can Switching to Self Lube Bearings Significantly Red...
Industry News- Can Switching to Self Lube Bearings Significantly Red...In the modern industrial landscape, the relentless pursuit of operational efficiency has led engineers to re-evaluate the most fundamental c...
-
 Industry News- How Does a Bronze graphite bearing Maintain Consisten...
Industry News- How Does a Bronze graphite bearing Maintain Consisten...In heavy industrial applications where liquid lubricants vaporize or carbonize, the Bronze graphite bearing stands as a critical engineering...
-
 Industry News- How to Accurately Calculate the Wear Life of a Self L...
Industry News- How to Accurately Calculate the Wear Life of a Self L...In the field of heavy-duty mechanical engineering, the reliability of a self lubrication bearing is critical for minimizing downtime and mai...
-
 Industry News- How Do Self Lube Bearings Compare to Traditional Grea...
Industry News- How Do Self Lube Bearings Compare to Traditional Grea...In the demanding landscape of heavy industrial machinery, the choice between lubrication systems can dictate the entire lifecycle of a mecha...
-
0+Establishment
Founded in 2014, Shuangnuo has 10 years of experience in the industry.
-
0+Advanced Equipment
Strong production capacity ensures that we can organize material production for customers as soon as possible and shorten the production cycle.
-
0+Happy Clients
There are more than 5,000 cooperative customers around the world.
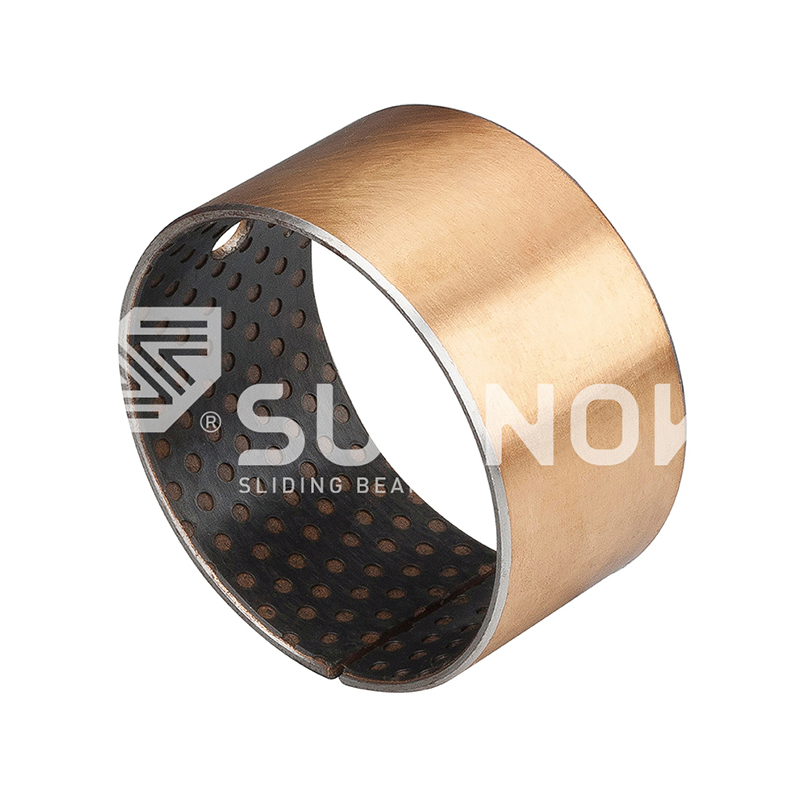
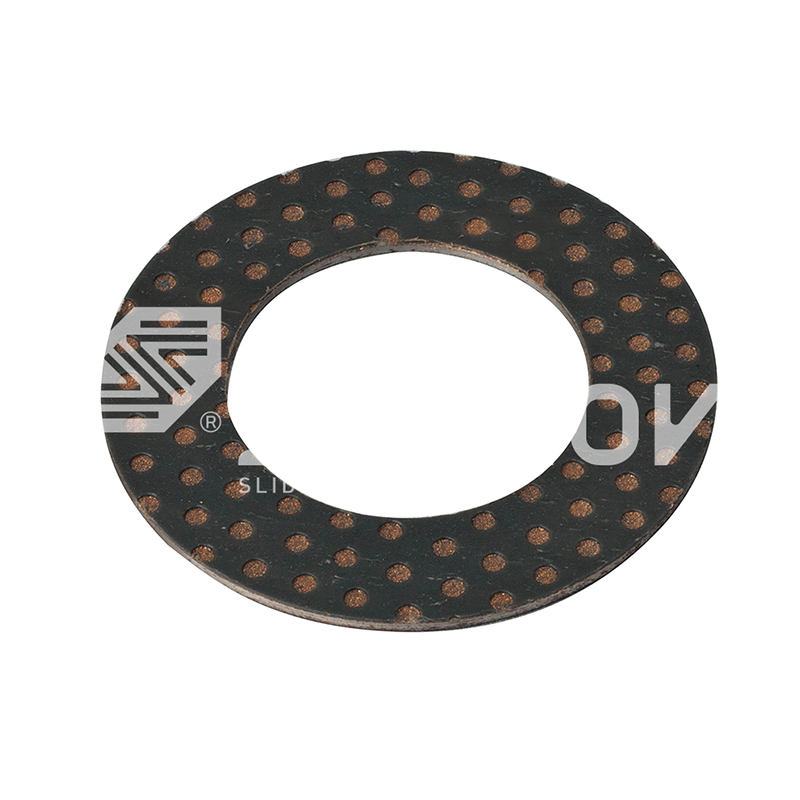
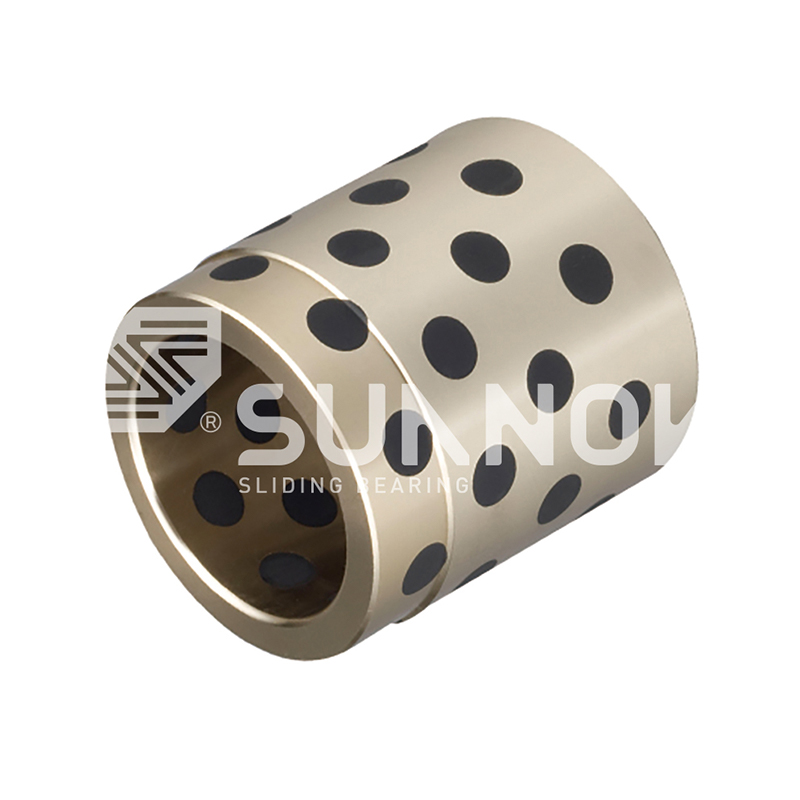
How to choose the right SF-2 bearing for a specific application?
When choosing a SF-2 boundary lubrication bearing for a specific application, there are several key factors to consider:
1. Load requirements
Static and dynamic loads: Determine the static and dynamic loads that the bearing will be subjected to during operation. SF-2 bearings perform well under high load conditions, so it is necessary to confirm that their load-bearing capacity meets actual requirements.
2. Speed
Operating speed: Evaluate the speed in the application. SF-2 bearings are generally suitable for low-speed or medium-speed applications. Make sure the selected bearing can withstand the actual speed range.
3. Lubrication conditions
Lubrication method: Select the lubrication method based on the application environment. SF-2 bearings are generally suitable for boundary lubrication conditions to ensure that they can still operate normally in the absence of sufficient lubrication.
4. Operating environment
Temperature range: Confirm the temperature of the operating environment. SF-2 bearings are generally suitable for temperatures ranging from -40°C to +100°C, and special applications may require higher or lower temperatures.
Corrosion and contamination: Consider chemicals, moisture and contaminants in the environment, which may affect the performance and life of the bearing.
5. Material selection
Material type: SF-2 bearings are usually made of wear-resistant alloy or polymer materials. Choose the right material to meet specific friction and wear requirements.
6. Installation and maintenance
Installation space: Consider the installation space and method of the bearing to ensure that the bearing can be installed smoothly and can be easily accessed during maintenance.
Maintenance requirements: Choose a bearing design that is easy to maintain and replace to simplify maintenance work in long-term use.
7. Bearing size
Dimension standard: According to the design requirements of the specific equipment, choose the appropriate bearing diameter and width to ensure compatibility with the shaft and its mating surface.
What are the common faults of SF-2 bearings and how to prevent them?
SF-2 boundary lubrication bearings may encounter some common faults in applications. Understanding these faults and their prevention measures can effectively extend the service life of the bearings. The following are some common faults and their prevention methods:
1. Wear
Fault description: Due to friction and lack of adequate lubrication, the bearing surface may wear, resulting in performance degradation.
Preventive measures:
Ensure proper lubricant use, check and replace lubricants regularly.
Control operating temperature to avoid overheating that causes lubricant degradation.
Ensure the load is within the rated range and avoid overloading.
2. Overheating
Fault description: The bearing generates too much heat during operation, which may cause material performance degradation or even failure.
Preventive measures:
Regularly monitor the bearing temperature to ensure that it is within the safe range.
Ensure good heat dissipation conditions, and consider adding heat dissipation devices or improving ventilation.
Appropriately select lubricants to ensure that they have good high temperature resistance.
3. Failure or jamming
Fault description: Due to insufficient lubrication or contamination, jamming between bearing components affects operation.
Preventive measures:
Keep the bearing clean and avoid dust and impurities.
Check the lubrication status regularly to ensure sufficient lubricant.
Avoid sudden load changes to ensure smooth operation.
4. Corrosion
Fault description: Moisture or chemicals in the environment may cause corrosion on the bearing surface, affecting performance.
Preventive measures:
Select suitable materials and coatings to increase corrosion resistance.
Keep the working environment dry and clean to avoid contact with chemicals.
Perform regular inspections and maintenance to detect signs of corrosion in time.
5. Abnormal noise
Fault description: The bearing makes abnormal noise during operation, which may be due to wear or internal damage.
Preventive measures:
Perform regular listening inspections and handle abnormalities in time.
Ensure that the bearing is installed correctly to avoid noise caused by improper installation.
Check the lubrication status to ensure good lubrication.
6. Peeling
Fault description: Metal peeling may occur on the bearing surface, usually due to overload or material defects.
Preventive measures:
Strictly control the workload and avoid overload operation.
Select high-quality bearing materials and avoid using inferior products.
Check the status of the bearing regularly and replace damaged parts in time.
7. Misalignment
Fault description: Due to improper installation or equipment structure problems, the bearing may be misaligned, causing additional wear and failure.
Preventive measures:
Ensure accurate alignment during installation, which can be corrected using alignment tools.
Check the bearing alignment status regularly to ensure there is no displacement or deviation.
Ensure the overall structure and support of the relevant equipment is stable.